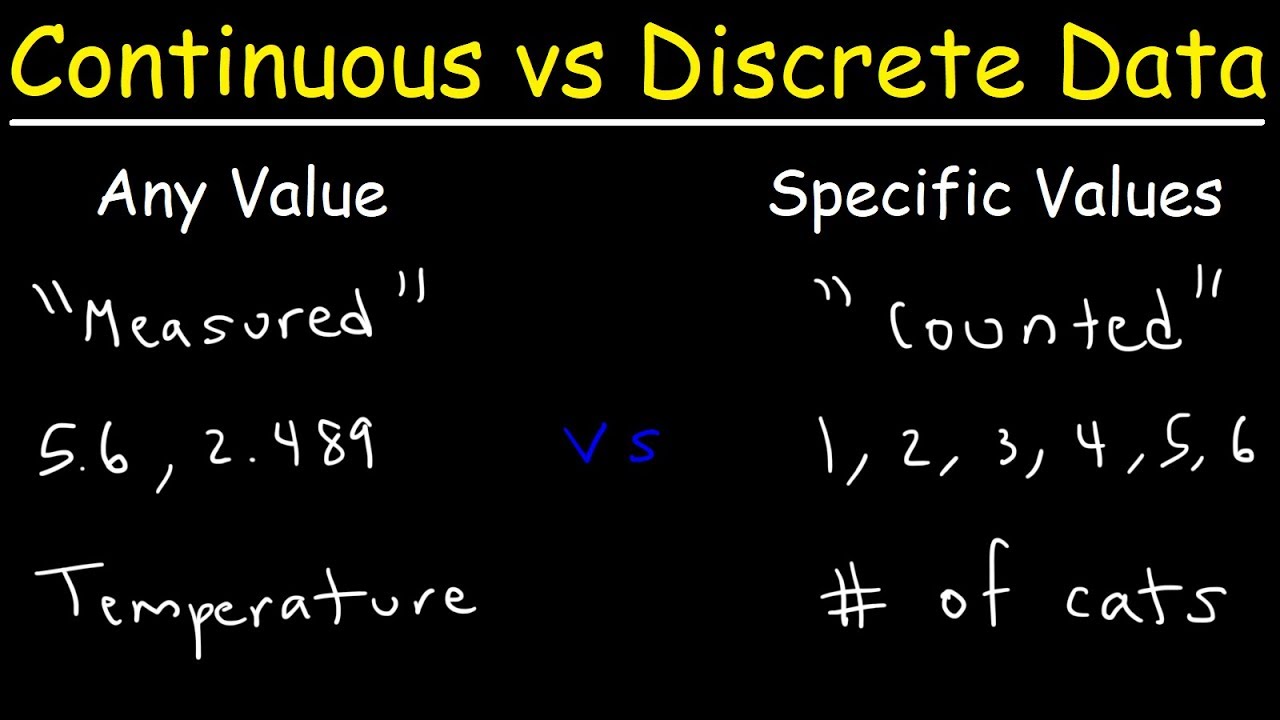
Is Temperature Discrete Or Continuous Data. Discrete and continuous data are both quantitative data. It has wide range and its value is true for all real numbers.
Continuous data can be further classified as measured on an interval scale or a ratio scale. Data that can be counted and has finite values is known as discrete data. Briefly explain why experiments having faulty design or inconsistent data are problems for scientists.
Continuous Data Sets Would Consist Of Values Like Height, Weight, Length, Temperature, And Other Measurements Like That.
Continuous data is data that falls in a continuous sequence. Why is population density a continuous data type when it is typically measured for aggregate areas such as census tracts or districts/neighbourhoods (ie, it can’t be measured at any point on a surface like gradient or temperature). Data that can be counted and has finite values is known as discrete data.
Continuous Data Is Considered The Complete Opposite Of Discrete Data.
Discrete and continuous data are easily representable in graphs. 5 degree celsius, here 30. The continuous variables can take any value between two numbers.
Examples Of Continuous Data Are Those That Are Typically Measured Like Temperature, Pressure, Humidity, Length, Time Etc.
The two data types are also sometimes qualitative. Temperature can have decimal values too as 75.3 f 30.2 c etc. Discrete and continuous data are both quantitative data.
Please Help Me With The Following:
Discrete data is the type of data that has clear spaces between values. A categorical or discrete variable is one that has two or more categories (values). Continuous data can be further classified as measured on an interval scale or a ratio scale.
If You “Measure” Temperature As Comfortable Or Uncomfortable It Should Be Considered Nominal.
They're things that can be measured in fractions and decimals. For example, temperature as a variable with three orderly categories (low, medium and high). In general, quantities such as pressure, height, mass, weight, density, volume, temperature, and distance are examples of continuous random variables.
Related Posts
- 5 Elements That Are Gases At Room Temperature5 Elements That Are Gases At Room Temperature. Elements can be classified based on physical states, often referred to as the aggregate state of an el ...
- Temperature 39 Celsius To FahrenheitTemperature 39 Celsius To Fahrenheit. How many fahrenheit in 39.2 °c. 101 rows convert 39 celsius to fahrenheit what is 39 celsius in fahrenheit?39 C ...
- To Erase An Entire Entry In A Cell And Then Reenter The Data From The Beginning Press The KeyTo Erase An Entire Entry In A Cell And Then Reenter The Data From The Beginning Press The Key. If you have the cell already opened for editing, you c ...
- Which Is True For Protecting Classified DataWhich Is True For Protecting Classified Data. Which of following is true of protecting classified data ? The correct answer to “which of the followin ...
- What Are Two Services Performed By The Data Link Layer Of The Osi Model Choose TwoWhat Are Two Services Performed By The Data Link Layer Of The Osi Model Choose Two. Specifically the data link layer performs two basic services: Pro ...


